Ready for the Challenge
Innovative solutions supporting in wound infection prevention and management
Holistic approach in wound infection prevention and management
Management and prevention
- Optimising the host response and treating the underlying pathology
- Reduce wound microbial load
- Promote environmental and general measures such as clean work environment and education
Cleansing with Granudacyn
Why use Mölnlycke antimicrobial dressings for wound care?
Proven to protect against infection and reduce bioburden
We know that when it comes to challenging wounds, you can’t leave anything to chance. That’s why our silver dressings are always supported by high-quality evidence.
 Less pain and trauma – not only at dressing changes
Less pain and trauma – not only at dressing changes
Only Mölnlycke® dressings combine the power of silver with Safetac® , a technology proven to minimise pain to patients and trauma to wounds
 Cost-effective treatment
Cost-effective treatment
Shorter healing times, shorter hospital stays, fewer dressing changes, a reduced need for analgesia during dressing changes and reduced bioburden

The antimicrobial advantage
Antibiotic resistance is a global problem. That’s why many clinicians today advocate for antimicrobial stewardship
Evidence shows that antiseptics such as antimicrobial dressings are both potent and rapidly effective
The evidence base for silver in wound management is significantly better than commonly perceived. If used selectively, silver not only has antimicrobial effects but is also characterised by an improvement in quality of life and good cost effectiveness
When to use our silver dressings
We believe that the major roles for our antimicrobial dressings are to:
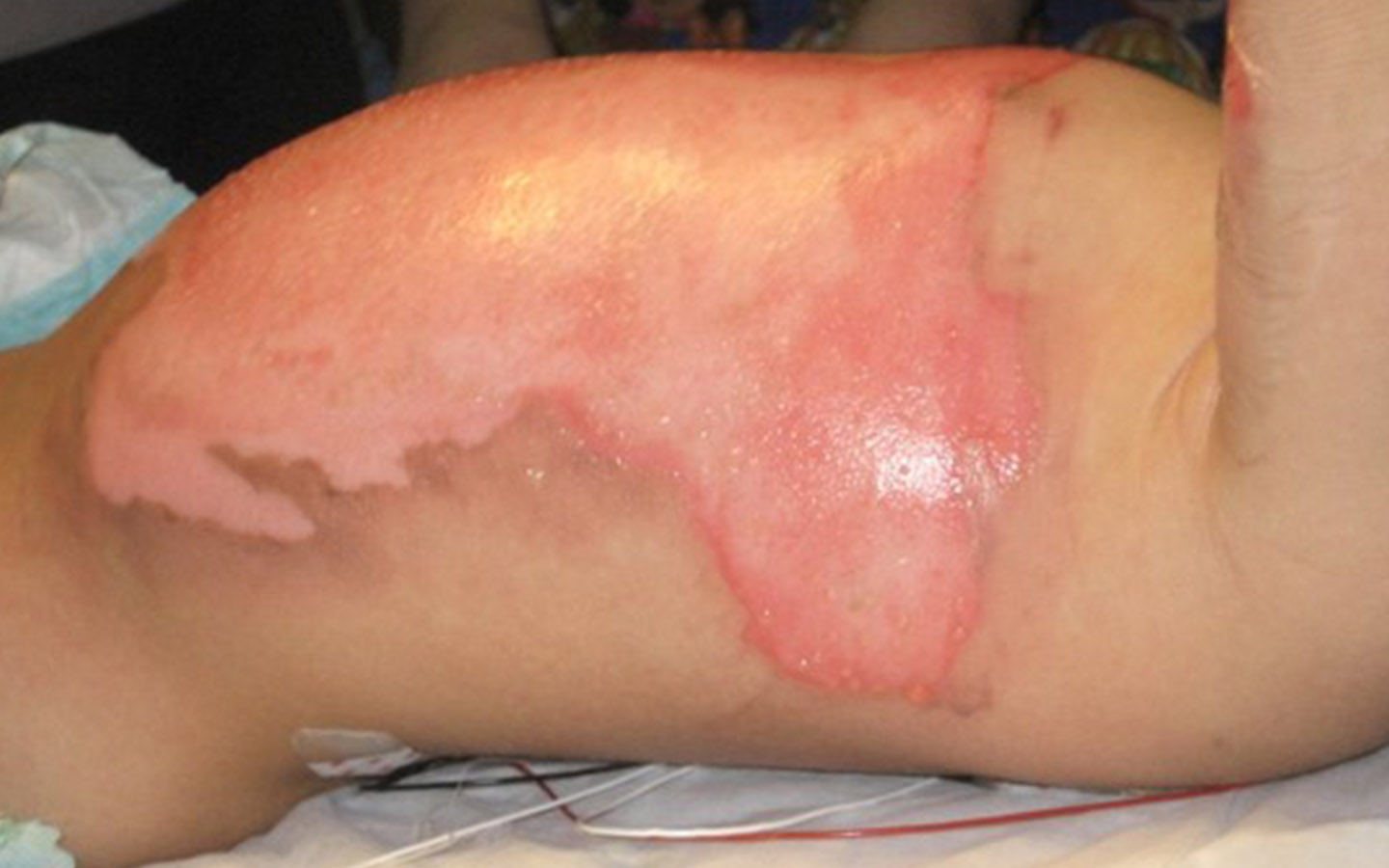
1. Act as an antimicrobial barrier for acute or chronic wounds at high risk of infection or re-infection. This may include burns, surgical wounds or wounds in patients who are immunocompromised or have poor circulation
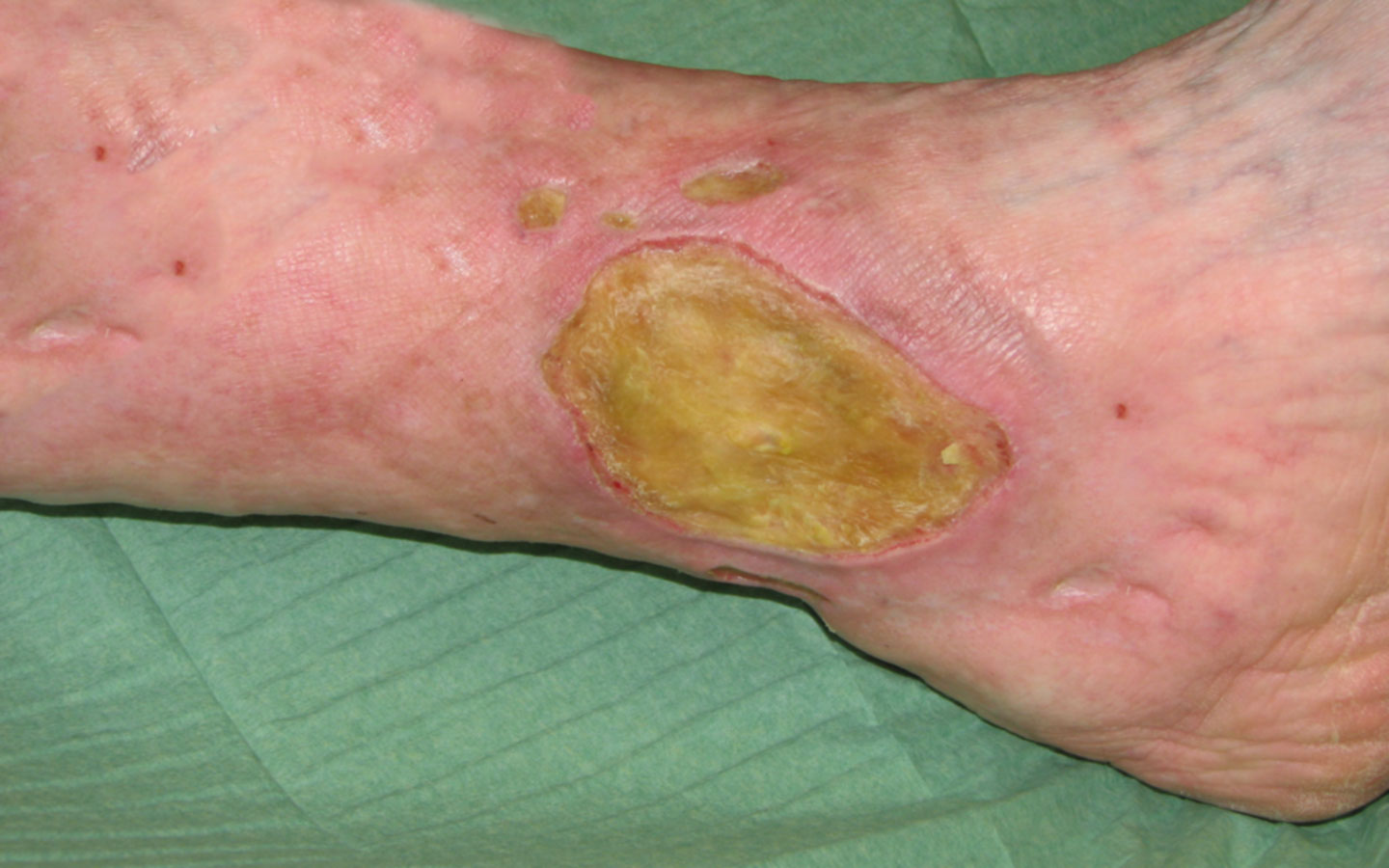
2. To reduce bioburden in chronic or acute wounds that are infected or are being prevented from healing by microorganisms
Education
Related Mölnlycke Advantage webinarsTalk to us about Antimicrobial products and how they can make a difference to your patients, team and budget

'References'